Top 10 Construction Innovations Transforming the Future of Building in the USA

Introduction
The U.S. construction industry is under pressure from labor shortages, rising costs, sustainability goals, and demand for speed and resilience. To meet these challenges, new materials, technologies, and processes are being adopted more rapidly than ever. This article reviews the top 10 innovations that are transforming how buildings are designed, constructed, and operated — why they matter, how they’re being used, and where you’re already seeing them in action.
Innovation Overview
The construction landscape in the United States is evolving faster than ever, driven by new technologies, smarter materials, and sustainability goals. Here are the ten innovations leading this transformation:
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) bring the digital model to life — improving training, safety, and design visualization.
- 3D Printing (Additive Construction) is revolutionizing how we build concrete structures — speeding up fabrication, cutting labor costs, and reducing material waste.
- Modular and Off-Site Construction brings factory precision to the building process, allowing faster assembly, higher quality, and less on-site disruption.
- Mass Timber offers a greener alternative to steel and concrete, combining strength, sustainability, and natural aesthetics in multi-story buildings.
- Robotics and Automation are stepping onto job sites, handling repetitive and dangerous tasks while improving efficiency and worker safety.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Advanced Building Information Modeling (BIM) are streamlining design, planning, and project management with predictive insights and automation.
- Net-Zero and High-Performance Buildings are reshaping design goals by integrating renewable energy, efficient systems, and climate-conscious materials.
- Self-Healing and Advanced Concrete Materials extend infrastructure life by repairing micro-cracks automatically and reducing maintenance needs.
- Drones, LiDAR, and Reality Capture technologies provide accurate site data, monitor progress in real time, and improve coordination between teams.
- Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Sensors enable real-time monitoring of structural health, environmental conditions, and energy performance.
Detailed Innovation Breakdown
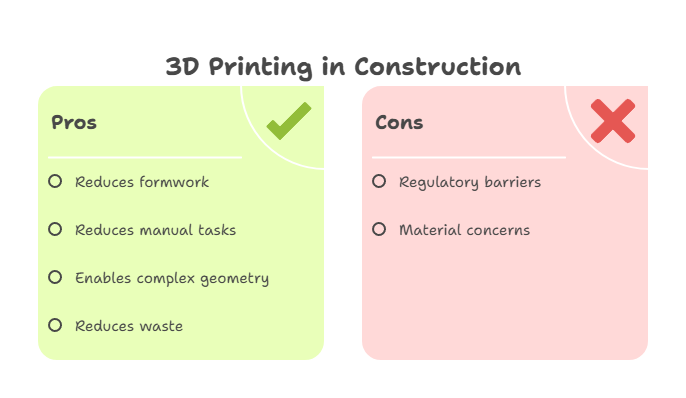
1. 3D Printing / Additive Construction
- Definition & Use: Building structural elements (walls, partitions, forms, structural components) using robotic 3D printing methods.
- Why It Matters: It reduces formwork, reduces manual tasks, enables complex geometry, and can reduce construction waste.
- Example & Status: Projects in the U.S. are experimenting with 3D-printed concrete homes / small commercial structures. One recent AP News article explored the potential for 3D printing to help with the housing crisis. AP News
- Considerations: Regulatory / code acceptance remains a barrier in many jurisdictions. Material properties & long-term durability must be verified.
2. Modular & Off-Site Construction
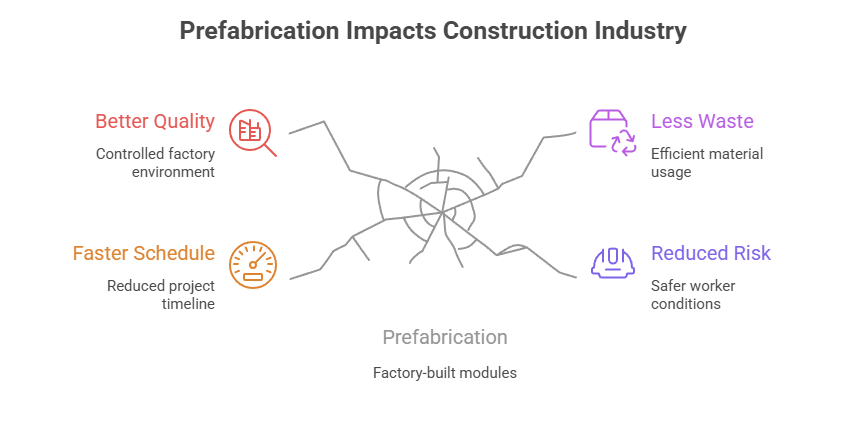
- What It Is: Prefabrication of modules, panels or even whole rooms in factories, then shipping to site for quick assembly.
- Why It Matters: Shorter project schedule, better quality control (factory vs weather-exposed onsite work), less waste & reduced worker exposure risk.
- Growth Trend: The modular & prefabrication sector is growing quickly; some reports say the modular construction market is projected to expand substantially through 2030. ConstructionPlacements
- Challenges: Transportation logistics, connection to utilities, coordination with site-built interfaces, and local code reviews.
3. Mass Timber / Engineered Wood
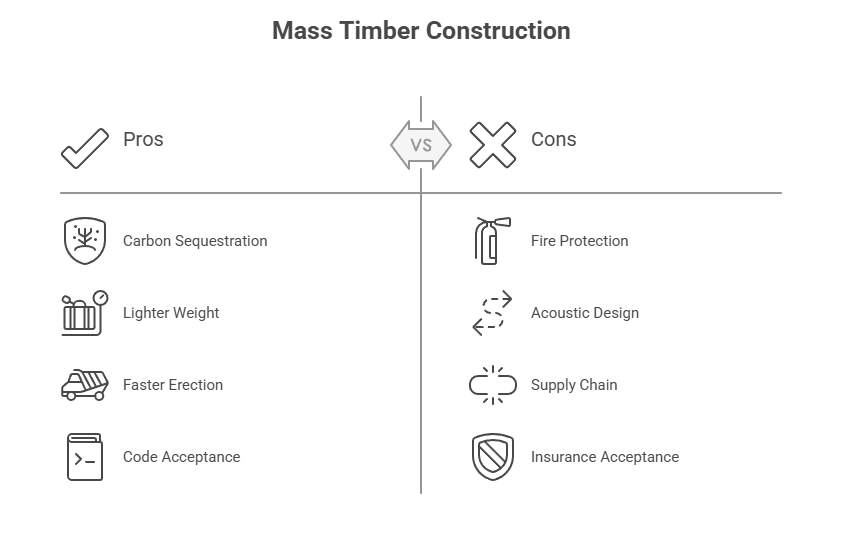
- What It Is: Use of engineered wood products such as cross-laminated timber (CLT), nail-laminated timber (NLT), glue-laminated beams in place of steel / concrete — for floors, walls, roofs.
- Why It Matters: Mass-timber structures sequester carbon (embodied carbon), are lighter, often faster to erect, and increasingly accepted in code / updated building standards.
- Where You See It: Multi-story wood buildings in U.S. cities (offices, residential) are becoming more common, especially where sustainability is part of the client’s goal.
- Trade-Offs: Fire protection requirements, acoustics / vibration design, supply of quality product & willingness of insurers / lenders to accept less-traditional materials.
4. Robotics & Automation on Site
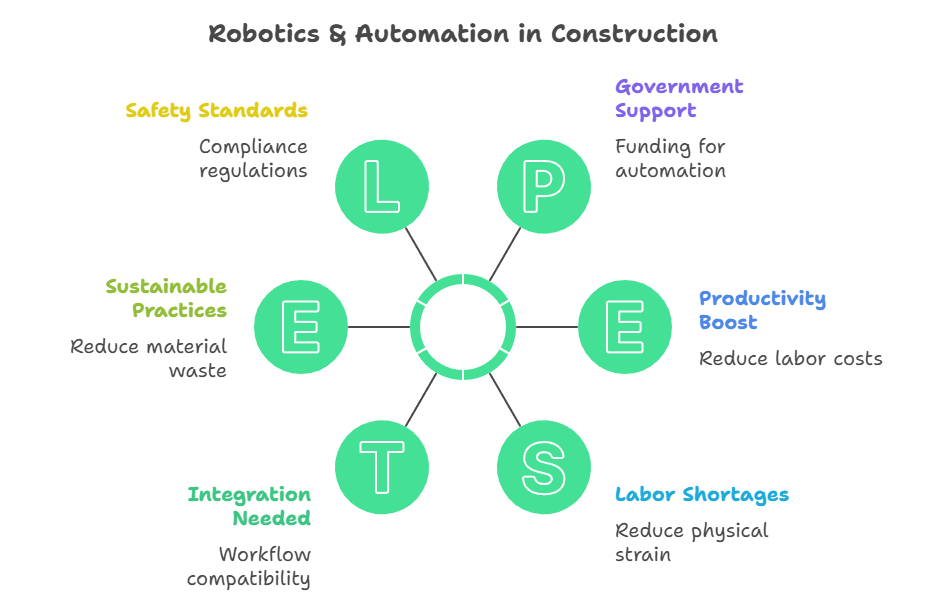
- Includes: Bricklaying robots, robotic rebar-tying tools, material handling automated vehicles / tele-operated machines, finishing bots for concrete surfaces, etc.
- Why It Matters: With labor shortages and need for higher safety & productivity, these robotic aids reduce the burden of repetitive tasks.
- Industry Signals: Industry / trend-watchers list robotics / AI-driven automation among the top emerging trends in 2025. Construction New York News+2Stronghold Engineering+2
- What Needs Attention: Integration with existing workflow, worker training, reliability & maintenance of robotic systems.
5. AI / Machine Learning + Advanced BIM

- What’s New: Increasing use of AI / ML for project scheduling / risk-forecasting / optimizing resource allocation; plus BIM enhancements (4D time schedules, 5D cost, 6D energy / sustainability data).
- Why It Matters: These capabilities help reduce cost overruns, minimize clashes, speed coordination, and improve decision-making.
- Data Point: One trade publication noted that AI adoption in construction increased to 37% in 2024, up from 26% in 2023. For Construction Pros
- Trend Momentum: NCCER reports that a large share of construction firms plan increased investment in AI for coming years. NCCER
6. Net-Zero & High-Performance Building Design
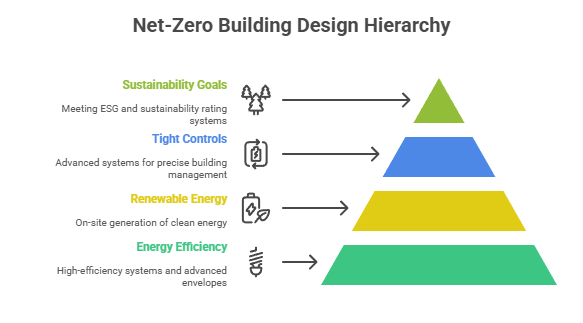
- What It Means: Design practices targeting net-zero energy consumption or high-efficiency systems + renewable energy generation + advanced building envelopes + tighter controls.
- Why It Matters: Operating cost savings over time, alignment with state / federal sustainability targets, resilience to regulatory changes and climate stress.
- Drivers: Growing pressure on developers / owners to meet ESG goals / sustainability rating systems. Also, code updates in many U.S. jurisdictions increasingly require tighter efficiency performance.
7. Self-Healing & Advanced Concrete Materials
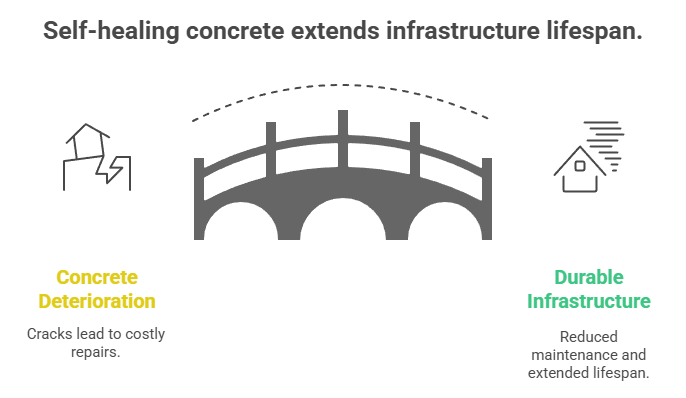
- Concept: Concrete mixes enhanced with additives — bacteria, micro-capsules, polymers — that allow small cracks to seal themselves or slow deterioration.
- Why It Matters: Reduces long-term maintenance / repair costs; extends lifespan of key structural elements and infrastructure.
- Status: Much of it is still in R&D / pilot phase, but increasingly being tested in bridge decks, façade panels, specialty concrete pours.
8. Drones / LiDAR / Reality Capture
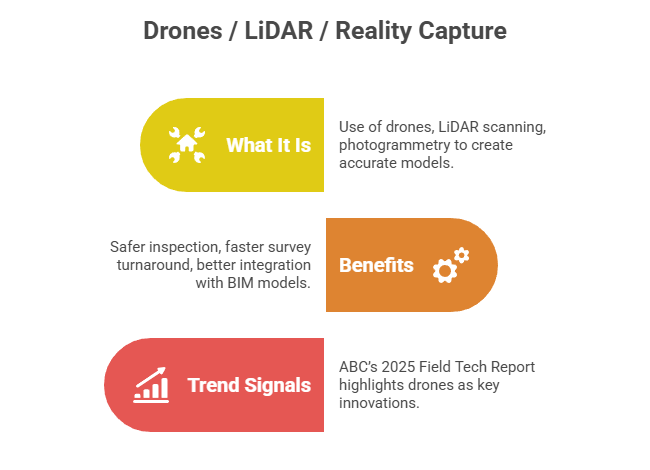
- What It Is: Use of drones (UAVs), LiDAR scanning, photogrammetry to create accurate as-built models, monitor progress, and support quantum take-offs.
- Benefits: Safer inspection (heights / facades), faster survey turnaround, better integration with BIM models for clash detection or progress verification.
- Trend Signals: ABC’s 2025 Field Tech Report highlights drones & connected systems as key jobsite-level innovations. For Construction Pros
9. IoT / Smart Sensors & Structural Health Monitoring
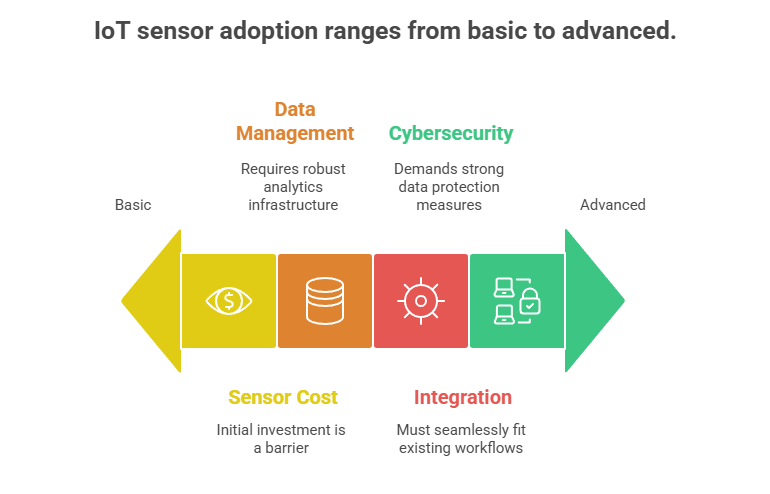
- Description: Embedding sensors into building materials, structural frames, HVAC / MEP systems to monitor temperature, humidity, strain / stress, vibration or load over time.
- Why It Matters: Enables predictive maintenance, helps catch performance drift (moisture intrusion, settlement, leaking), and supports data-driven facility management decisions.
- Adoption Considerations: Sensor cost, data management / analytics, integration with maintenance workflows, cybersecurity / data privacy issues.
10. Augmented Reality (AR) & Virtual Reality (VR)
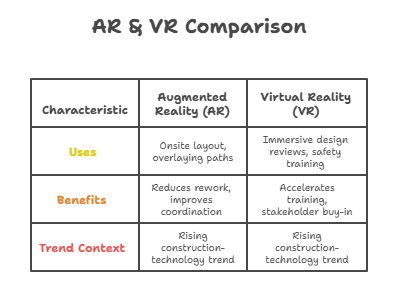
- Uses: AR headsets / tablets for onsite layout, overlaying piping or conduit paths, or machine-guidance lines; VR for immersive design reviews, safety & equipment training.
- Benefits: Reduces rework, improves coordination / stakeholder buy-in (owners, contractors), accelerates training for new workers or hazardous equipment.
- Trend Context: AR / VR is cited among the rising construction-technology trends in 2025. calpcc.com+1
Visualizing the Impact
Here’s a suggested bar-chart idea you could embed:
| Innovation | Relative Impact on Schedule | Impact on Cost | Sustainability / Carbon Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modular Construction | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| AI / BIM / ML | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ |
| Mass Timber | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★☆ |
| Robotics / Automation | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
*Scale: ★ = modest impact; ★★★★ = high impact
Replace with actual numeric data if you have access to project-based KPIs.
You could also plot a radar-chart comparing the same innovations over those three impact dimensions.
Getting Started: Tips for Engineers, Builders & Entrepreneurs
- Pilot small projects first. Try one of these innovations on a small scale (e.g. a modular component or sensor network on a building) to test ROI before wide rollout.
- Include innovation in early design. Technologies like AI / BIM, mass timber, modular systems or sensor integration must be part of the concept / schematic design phase to get full benefit.
- Engage with local building codes & permitting authorities early. Some innovations (3D-printed concrete, new sensor-infrastructure systems) require approvals or documentation to satisfy safety & compliance.
- Upskill your team. AR/VR training, digital-tool proficiency, and maintenance of sensor / robotics systems require new skills; plan for training (or partner with technology providers).
- Track metrics over lifecycle. Set baseline KPIs (schedule duration, defect rate, maintenance cost, energy use) so you can measure whether the innovation delivered what you expected.
Why This Matters for the USA
Together, these innovations help the U.S. construction industry meet multiple pressures at once: rising material / labor costs, carbon / sustainability targets, labor shortages, and demand for faster project delivery. They also help shift the industry toward more resilient, data-driven and sustainable building practices. Stakeholders including architects, engineers, contractors, developers and regulators all have a role to play — and early adopters may gain competitiveness as codes, markets and client expectations evolve.
References
Here are key sources for data & trends referenced above:
- For Construction Pros — “Top 10 Construction Technology Trends to Watch in 2025” For Construction Pros
- NCCER — “Construction Industry Trends for 2025” NCCER
- Construction NY News — Shaping Tomorrow: Top Construction Trends for 2025 Construction New York News
- Stronghold Engineering — Top Construction Industry Trends 2025 Stronghold Engineering
- ABC (Associated Builders & Contractors) — 2025 Field Tech Report For Construction Pros
- GlobeNewswire — “United States Construction Industry Report 2025: A … Forecasted Market by 2029” GlobeNewswire
You may be interested in: Saudi Arabia Unveils the World’s First “Sky Stadium”




Responses